
Tags: Economy WTO WTO Public Stockholding MSP Economic Growth Masala Bond Environmental Performance Index Forecast of Economic Growth Functions of the Finance Commission
The measure of Human Development Index (HDI) is utilized by the United Nations (UN) to assess nations for the well-being and prosperity of their residents. Before the formation of the Human Development Index (HDI), a nation's degree of improvement was normally estimated utilizing monetary measurements, especially the GNI or, the gross national income. The UN accepted that financial measures alone were lacking for surveying improvement since they didn't necessarily in all cases mirror the personal satisfaction of a nation's typical residents. It established the HDI in 1990 to consider different factors and impart an all the more balanced assessment for human development.
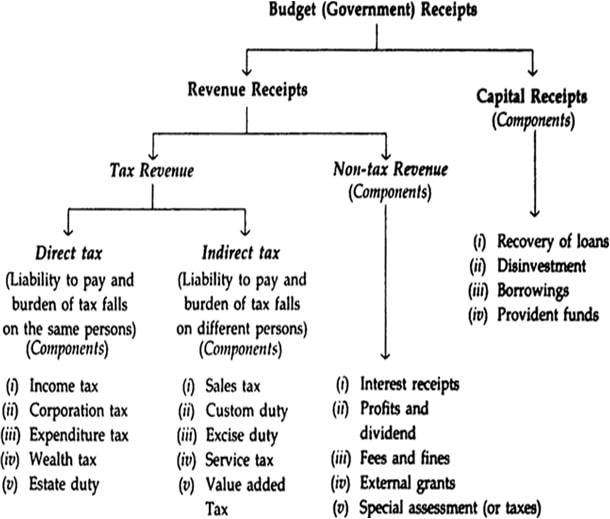
Taxes and other public funds collected as a result of the Federal Government exercising its sovereign or governmental powers constitute governmental receipts. The surplus or deficit is the difference between government expenditures and receipts.
Revenue Receipts
These are government receipts that neither (i) reduce assets nor (ii) create liabilities. Taxes, interest and dividends on government investments, cess, and other government service receipts are all included in this category. These are the government's current income receipts from all sources. The means by which the government can spend its money is through revenue. According to Section 9.6, revenue receipts are further divided into tax revenue and non-tax revenue.
Capital Receipts
These are government receipts that either (i) create liabilities (such as borrowing) or (ii) reduce assets (such as disinvestment).Therefore, when the government. Referred to as a capital receipt, it raises funds either by incurring a liability or by selling its assets.
(A) Small savings deposits and borrowing from the Public Provident Fund are two examples of capital receipts that result in liability. How? (i) Borrowings are considered capital receipts because they increase the government's liability to repay loans; ii) PPF funds and small savings deposits in post offices and banks are also considered capital receipts because they increase the government's liability to repay these amounts to PPF holders and small savings depositors.
(B) Disinvestment and loan recovery are two capital receipts that reduce assets.D2006, 12C) How? (i) Selling a portion or the governments entire stake in public sector companies like HMT, LIC, and FCI is considered disinvestment. Government assets are reduced by the funds raised by disinvestment. (ii) The recovery of a loan is also a capital receipt because it reduces government assets. For instance, if the UP government, which received a loan of Rs 100 crore from the Central government, repays Rs 20 crore, the Central government's assets now have a value of Rs 80 crore, down from Rs 100 crore.
Difference between capital gains and revenue
The fact that capital receipts are non-redeemable and the government is not obligated to return them is the primary distinction between revenue receipts and capital receipts. However, the government is obligated to return capital receiptswhich are borrowingsalong with interest.
Capital receipts that do not result in the creation of debt
Capital receipts may or may not result in the creation of debt. Receiving loans from foreign governments, net borrowing from the domestic government, and borrowing from the RBI are all examples of debt-creating receipts. Recovery of loans, proceeds from the sale of public enterprises (also known as disinvestment), and so on are examples of non-debt capital receipts. Debt is not created by these.